10 Ways to Ensure Compliance in Medical Injection Mold Production
The production of medical devices via injection molding demands rigorous compliance with global regulatory standards. From raw material selection to final sterilization, each process step must be validated and documented to ensure patient safety and product reliability.

1. Implement a Robust Quality Management System (QMS)
Medical molding manufacturers should establish a QMS aligned with ISO 13485:2016 and, where applicable, FDA 21 CFR 820. This system governs document control, supplier quality, traceability, change control, and corrective/preventive actions (CAPA) [1].
2. Integrate Thorough Risk Management (ISO 14971)
A compliant risk management system based on ISO 14971:2019 identifies, evaluates, and mitigates risks throughout the product lifecycle. This includes design, material selection, manufacturing, and post-market surveillance [2].
3. Vet and Monitor Suppliers
Suppliers must be audited and selected based on their compliance with ISO 13485 and biocompatibility standards such as ISO 10993. Critical suppliers of resins and tooling must maintain proper documentation, including certificates of analysis (CoA) and change notification systems [3].
4. Control Material Selection & Handling
Only materials certified as biocompatible per ISO 10993-1 and/or USP Class VI should be used. Proper traceability of lot numbers and secure storage under defined temperature/humidity conditions are essential to prevent contamination or degradation [4].
5. Maintain Cleanroom or Controlled Environments
Injection molding of medical components should occur in ISO 14644-1 certified cleanrooms (typically ISO Class 7 or 8). Regular particulate and microbial monitoring, gowning protocols, and HEPA filtration ensure a sterile-friendly production environment [5].
6. Validate and Control Process Parameters
Critical process parameters (CPPs) such as injection pressure, melt temperature, cooling time, and mold temperature must be controlled and validated via IQ/OQ/PQ protocols. Use Statistical Process Control (SPC) to monitor and maintain consistency [6].
7. Conduct In-Process and Final Inspection
Automated optical inspection (AOI), coordinate measuring machines (CMM), and functional testing validate product conformity. Non-conforming parts must be documented, quarantined, and investigated under the CAPA system [7].
8. Perform Biocompatibility & Leachables Testing
All medical-grade plastics must undergo biological evaluation under ISO 10993-1, including tests for cytotoxicity, sensitization, and leachables. Analytical methods like GC-MS and HPLC are used to assess extractables and potential patient exposure [8].
9. Ensure Sterilization Validation
Sterilization techniques (e.g., ethylene oxide, gamma irradiation, steam autoclave) must be validated following ISO 11135(EtO) or ISO 11137 (radiation). Bioburden testing, sterility assurance level (SAL) calculations, and residual analysis are mandatory [9].
10. Perform Internal Audits and Regulatory Readiness
Schedule routine internal audits and mock inspections based on regulatory frameworks such as the MHRA GxP guidelines and FDA 21 CFR 820. Maintain audit logs, SOPs, training records, and traceability documents to ensure readiness for unannounced inspections [10].
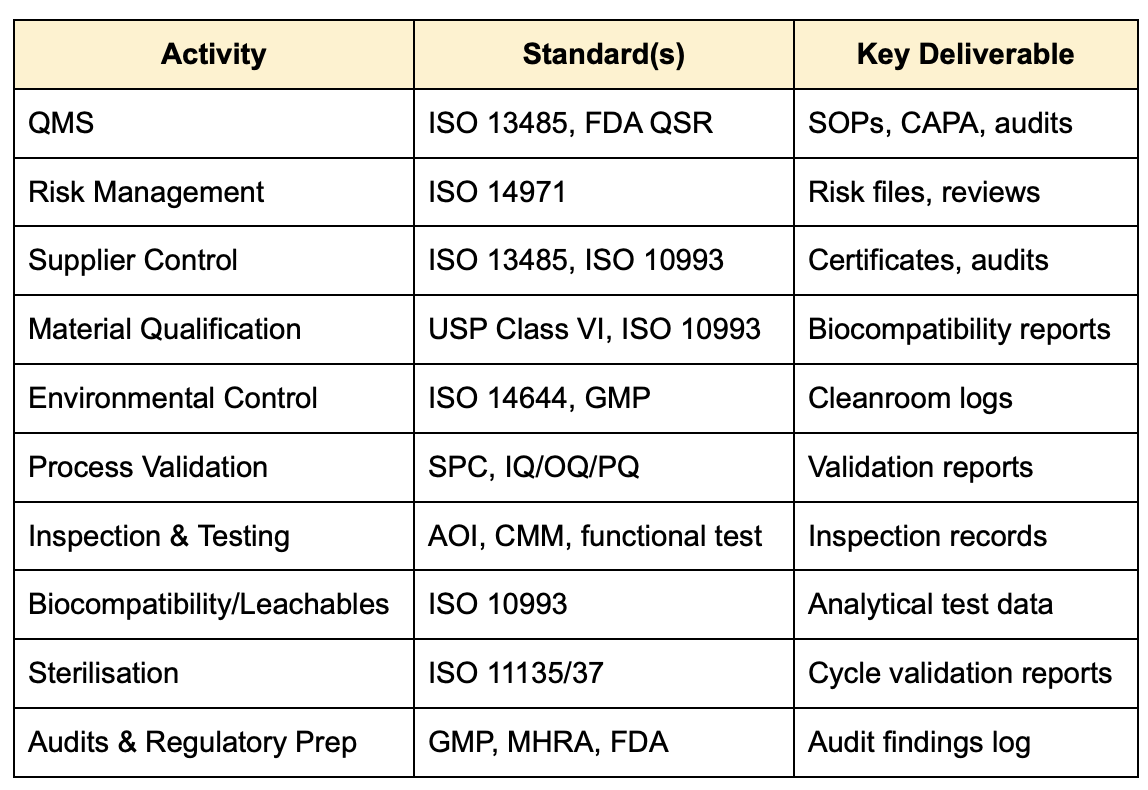
Summary Table of Key Standards and Activities
Partnering with Micro Systems provides customers with a strategic advantage in ensuring full compliance in medical injection mold production. As a certified ISO 13485 manufacturer, Micro Systems integrates rigorous quality management, precision tooling, and cleanroom injection molding under one roof, reducing compliance risk and enhancing traceability. Our in-house expertise in design for manufacture (DfM), process validation (IQ/OQ/PQ), and regulatory documentation ensures that every stage of production, from concept to final part, is aligned with global standards. With capabilities in high-precision micro molding and class 7 cleanroom environments, Micro Systems enables customers to meet stringent biocompatibility, sterility, and performance requirements while accelerating time-to-market through validated, scalable processes.
Contact us today!
References
[1] ISO 13485:2016 – Medical devices – Quality management systems – Requirements for regulatory purposes.
[2] ISO 14971:2019 – Medical devices – Application of risk management to medical devices.
[3] FDA 21 CFR Part 820 – Quality System Regulation.
[4] ISO 10993-1:2018 – Biological evaluation of medical devices – Part 1: Evaluation and testing.
[5] ISO 14644-1:2015 – Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments – Classification of air cleanliness.
[6] GHTF Process Validation Guidance (SG3/N99-10:2004) – Quality management systems – Process validation guidance.
[7] AAMI TIR33:2005 – Guide for the development, content and format of labelling for medical devices.
[8] USP <87> and <88> – Biological Reactivity Tests, in vitro and in vivo.
[9] ISO 11135:2014 – Sterilisation of health-care products – Ethylene oxide.
[10] MHRA Guidance on Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) and Good Distribution Practice (GDP).