Dimensional Stability in Medical Micro Molding: Controlling Shrink and Warpage
What Is Dimensional Stability in Medical Micro Molding?
Dimensional stability in medical Micro Molding refers to the ability of a component to maintain its intended geometry, tolerances, and functional performance during and after moulding. It is critical for microfluidic devices, minimally invasive surgical tools, and implantable components, where tolerances often fall below ±5 µm [1].

Why Do Shrinkage and Warpage Occur in Medical Micro Molding?
Shrinkage occurs due to polymer volume contraction during cooling and solidification [2]. Warpage results from differential shrinkage caused by non-uniform thermal distribution, polymer flow orientation, or asymmetric geometry [3][4]. Both defects compromise dimensional accuracy, potentially leading to device malfunction or regulatory non-compliance [5].
How to Control Shrinkage in Medical Micro Molding?
To minimize shrinkage in medical-grade polymers:
- Select low-shrinkage materials such as COC or polycarbonate for diagnostic and optical applications [6].
- For high-strength or implantable devices using PEEK or PP, implement annealing or post-mold heat treatment to stabilize dimensions [7][8].
- Optimize packing pressure and cooling rates to achieve uniform polymer density throughout the component.
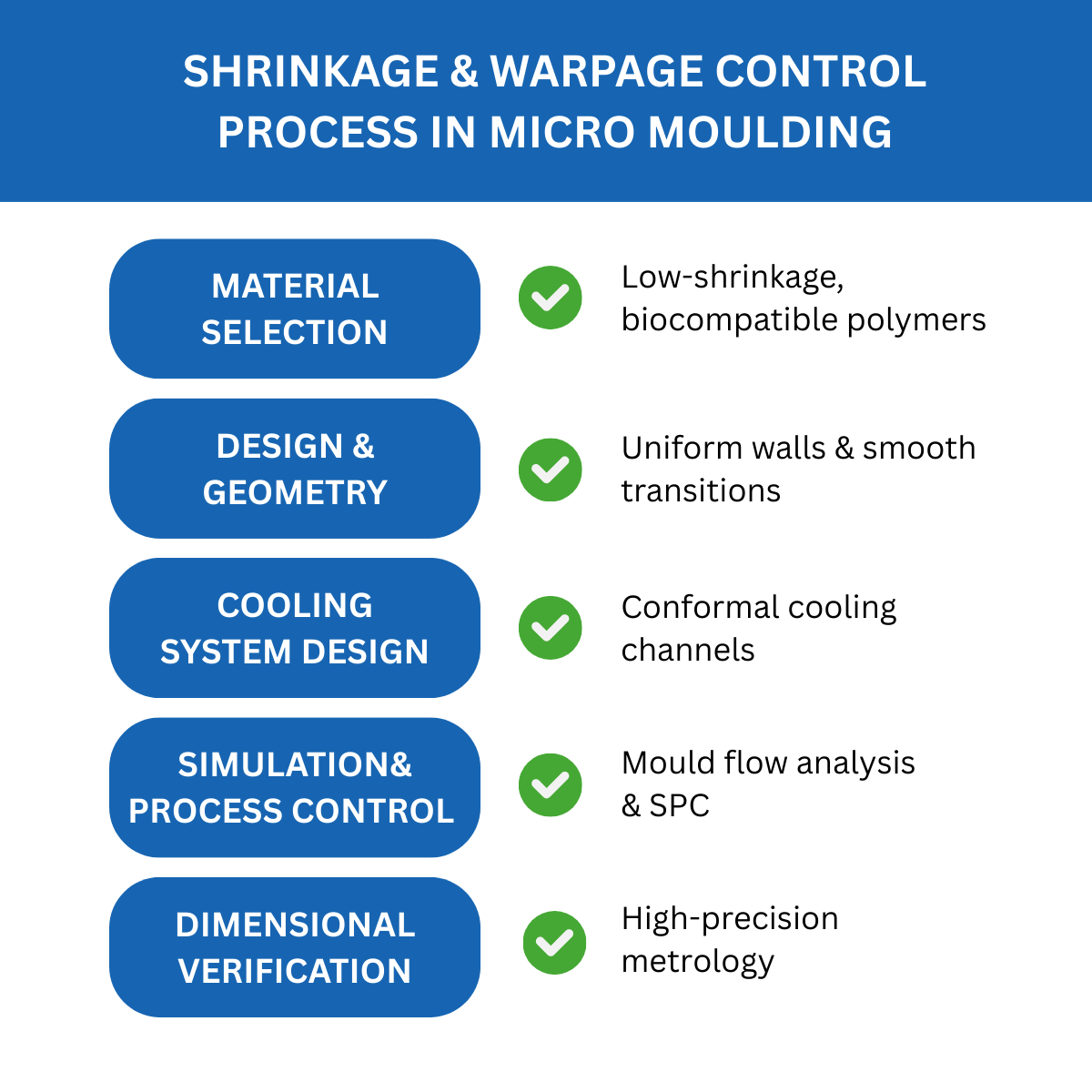
How to Prevent Warpage in Micro Medical Devices?
Warpage can be reduced by:
- Maintaining uniform wall thickness across critical areas [9].
- Incorporating fillets and smooth transitions to avoid stress concentrations [10].
- Using ribs or gussets for reinforcement without introducing localized cooling imbalances [11].
- Integrating conformal cooling systems that provide even temperature distribution [12][13].
Role of Conformal Cooling in Medical Micro Molding
Conformal cooling channels, often produced using additive manufacturing, closely follow the geometry of the medical component. This improves heat transfer efficiency, reduces cycle time, and prevents differential cooling, a key cause of shrinkage and warpage in precision molded parts [12][13].
Simulation and Process Control for Dimensional Stability
Mold-flow simulations predict potential shrinkage hotspots, pressure imbalances, and warpage-prone zones before tool fabrication [14].
- The most critical parameter for warpage reduction is mold temperature, followed by packing pressure and holding time [15].
- Statistical process control (SPC) and real-time cavity pressure monitoring ensure repeatable production under ISO 13485 and FDA 21 CFR Part 11 requirements [16].
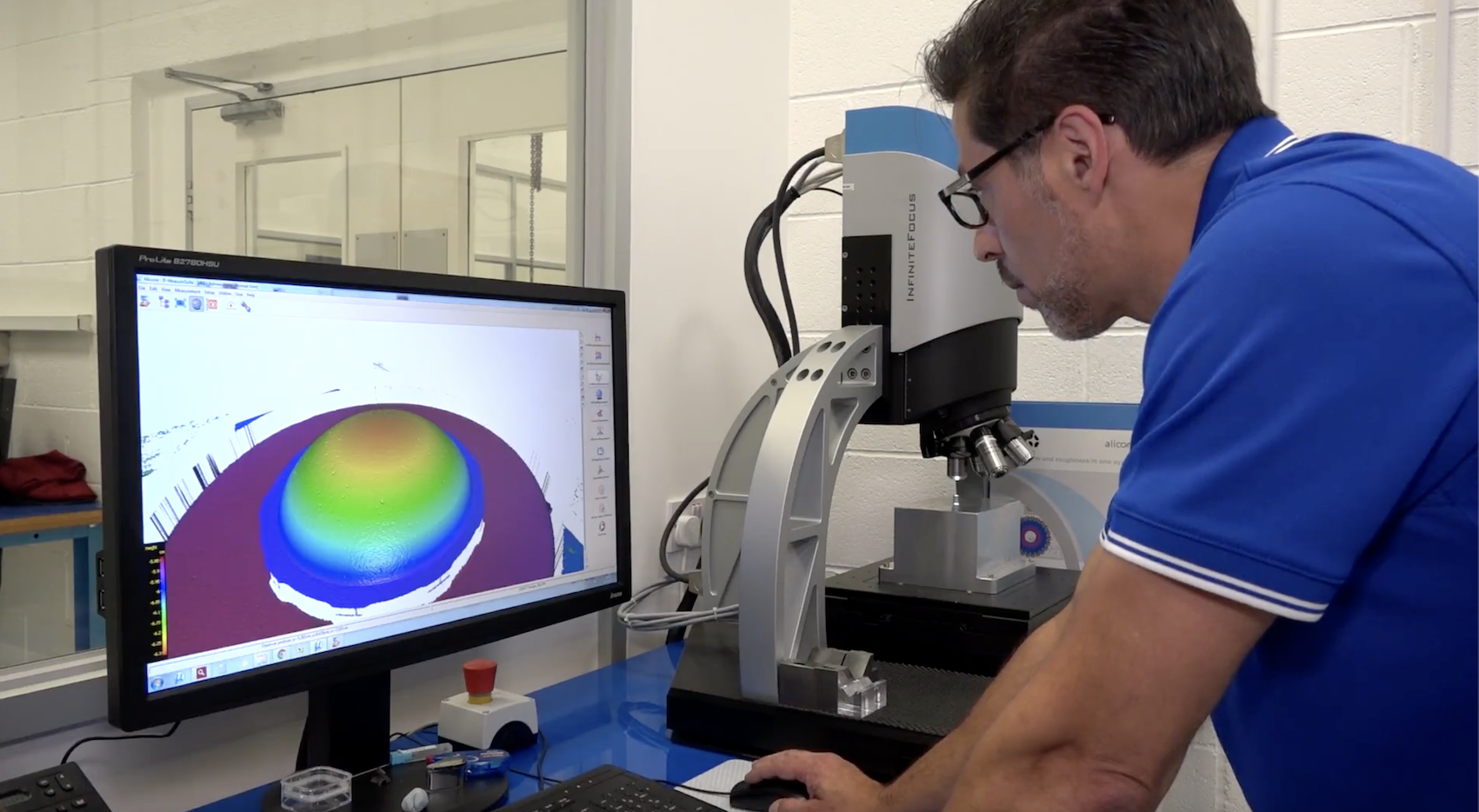
Dimensional Verification in Medical Micro Molding
High-precision metrology methods, such as optical profilometry, SEM, and confocal microscopy, are essential for validating micro-scale components without compromising sterility. These techniques are integrated into Gage R&R and IQ/OQ/PQ protocols during process validation [17].
Quick Answer: How to Reduce Shrinkage and Warpage in Medical Micro Molding?
- Choose biocompatible low-shrinkage materials.
- Design for uniform wall thickness and smooth transitions.
- Implement conformal cooling systems.
- Optimize mold temperature, packing pressure, and holding time.
- Validate with real-time process monitoring and precision metrology.
Micro Systems’ Capabilities in Medical Micro Molding
Micro Systems offers ultra-precision Micro Molding solutions for the medical sector, including sub-micron tooling tolerances, validated conformal cooling, and GMP-compliant ISO Class 7 cleanroom production. Their expertise in high-aspect-ratio components ensures minimal shrinkage and warpage in high-volume, regulatory-controlled environments.

FAQ: Dimensional Stability in Medical Micro Molding
Q: What materials are best for low-shrinkage medical Micro Molding?
A: COC, COP, and polycarbonate for diagnostics; PEEK for implants with post-mold annealing.
Q: Can conformal cooling really reduce warpage?
A: Yes, it provides uniform thermal management, reducing internal stress gradients that cause warpage.
Q: What tolerances can be achieved in medical Micro Molding?
A: Sub-micron to ±5 µm tolerances are achievable with validated tooling and process control.
Q: Is process validation mandatory for medical Micro Molding?
A: Yes, under ISO 13485 and FDA requirements, IQ/OQ/PQ validation ensures repeatable dimensional stability.
References
- Smith, J., Micro-Moulding Challenges in Medical Manufacturing, J. Med. Microengineering, 2024.
- Brown, P., Polymer Shrinkage Mechanisms in Injection Moulding, Plastics Tech Rev., 2023.
- Liu, Y., Flow-Induced Orientation in Semi-Crystalline Polymers, Polym. Proc. J., 2022.
- Chang, R., Thermal Gradients in Micro-Scale Medical Moulding, Int. J. Polym. Proc., 2022.
- ISO 13485:2016, Medical Devices – Quality Management Systems.
- SpecialChem, Shrinkage in Medical Injection Moulding, 2024.
- Alcamiglobal, High-Performance Polymers for Medical Micro-Moulding, 2024.
- FDA Guidance, Polymer Annealing in Medical Device Production, 2023.
- FirstMold, Warpage Prevention in Medical Components, 2024.
- Wikipedia, Plastic Component Design Principles, 2024.
- Polymer Moulding, Design for Medical Micro Components, 2024.
- Wikipedia, Conformal Cooling Channels in Medical Moulding, 2024.
- MDPI, Cycle Time Reduction with Conformal Cooling, 2023.
- Alcamiglobal, Simulation-Driven Medical Moulding, 2024.
- MDPI, Impact of Mould Temperature on Medical Warpage, 2023.
- FDA 21 CFR Part 11, Electronic Records in Medical Manufacturing.
- Alcamiglobal, Metrology in Micro Medical Devices, 2024.