Top Trends in Medical Injection Molding for 2025: Micro Molding, Automation & Sustainability
1) Micro molding becomes the standard for next-generation devices
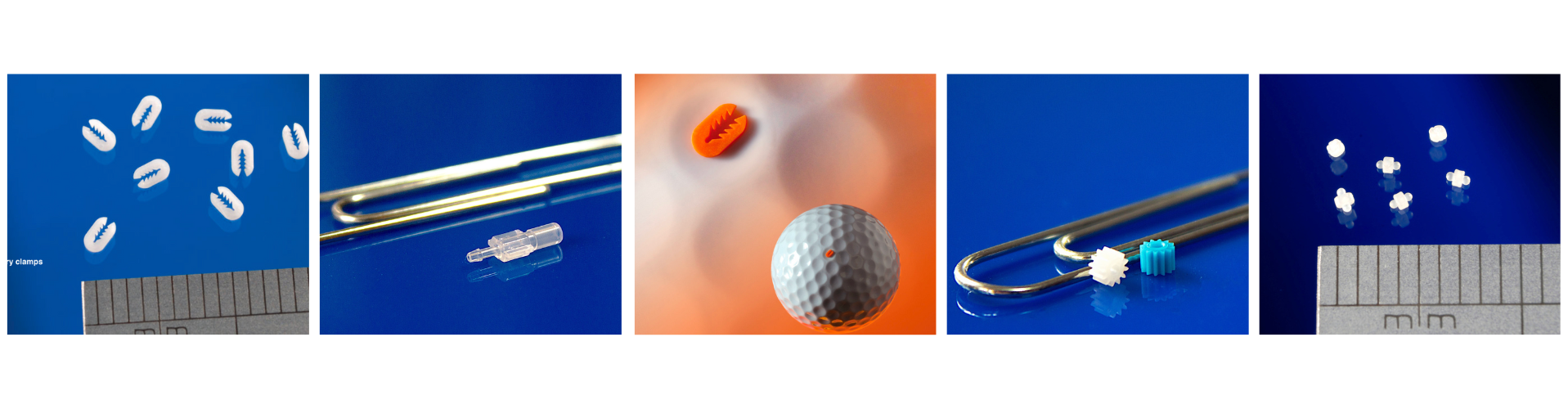
Why it matters: The rise of minimally invasive and wearable medical technologies requires components with micron-scale precision, tight tolerances (often below ±10 μm), and high surface finish while maintaining biocompatibility and sterilzation compatibility [1][2].
Where demand is rising:
- Minimally invasive and neurovascular devices
- Intraocular lenses (IOL) and ophthalmic delivery cartridges
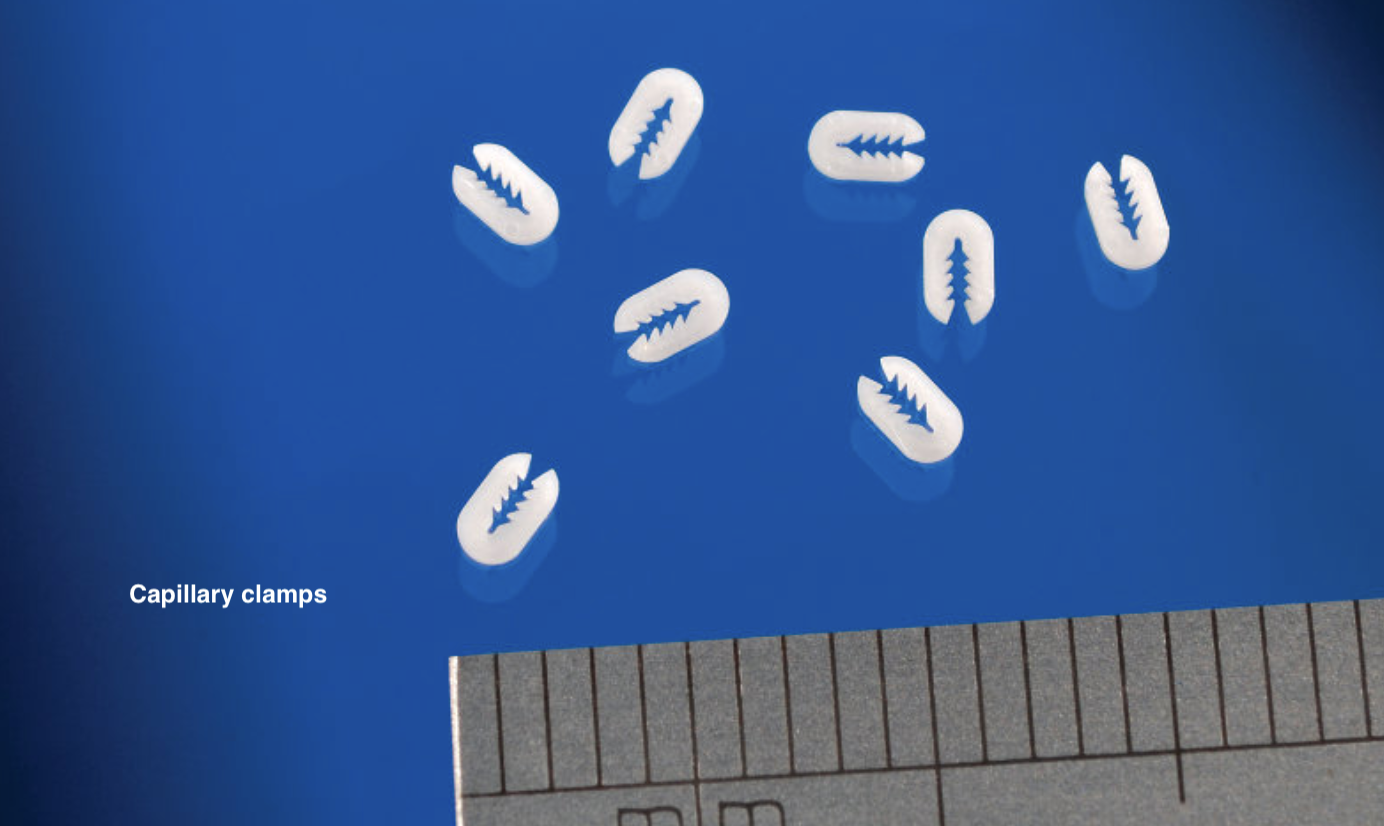
- Drug delivery components (micro-gears, valves, lattice features)
- Diagnostics and microfluidics (lab-on-a-chip, reagent reservoirs)
Analysts project robust growth for medical micro injection molding through 2030, driven by miniaturization and chronic care demand [3].
Engineering considerations for 2025:
- Tool steel selection and micro-venting strategies (<5 μm)
- Resin selection: COC/COP for optics, PEEK/LCP for structural parts, medical LSR for micro seals
- High-magnification in-line metrology and automated datum schemes

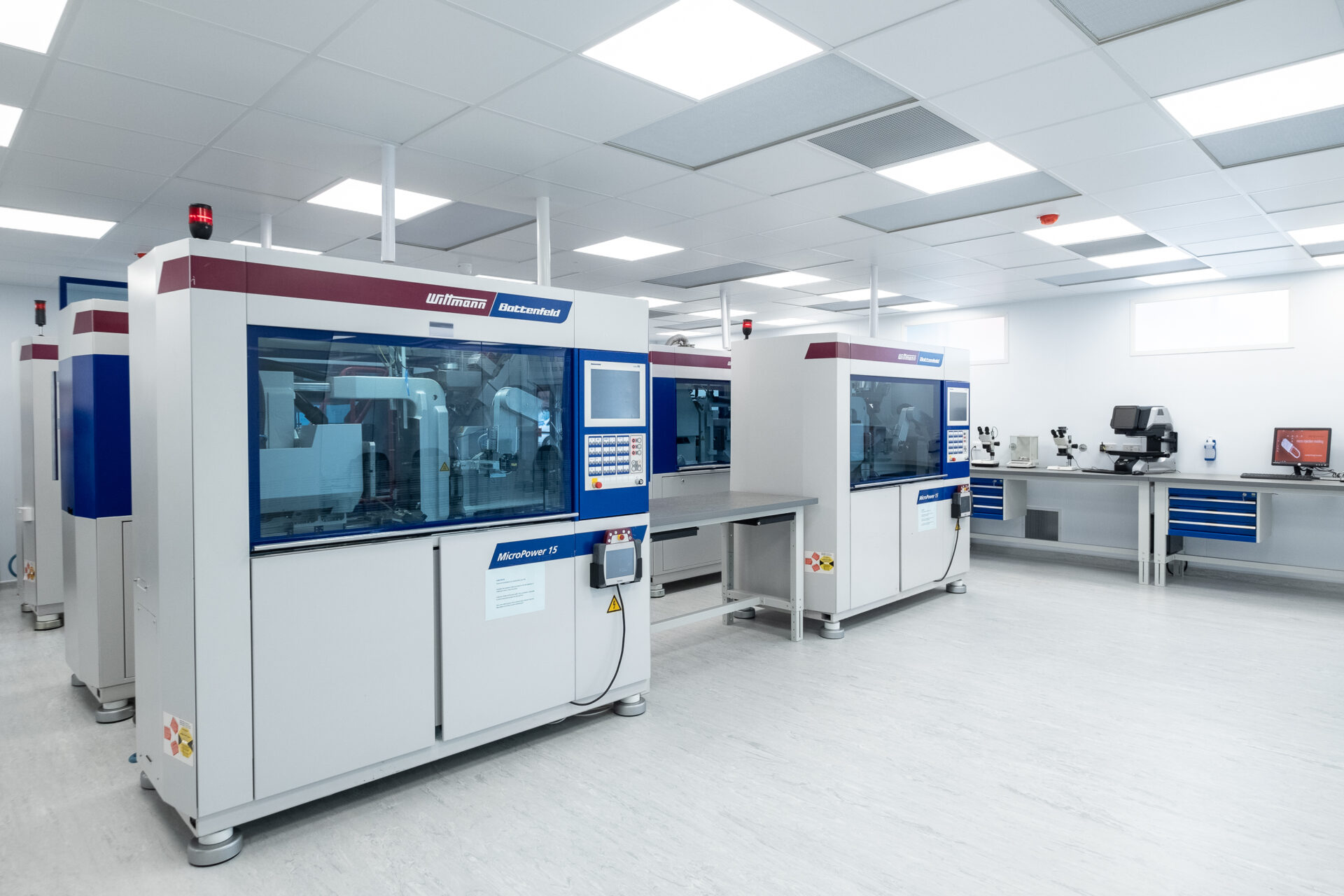
2) Automation and in-line quality take centre stage
What’s new: Automation is shifting from optional to essential in cleanroom molding cells. High-precision robotics, cavity-level process monitoring, and machine vision systems are increasingly deployed to ensure zero-defect output [4].
Key developments:
- Automated degating, deflashing, and kitting within ISO Class 7/8 cleanrooms
- Cavity pressure and temperature sensors integrated with closed-loop control
- Digital twins to stabilize Cp/Cpk before PPAP
- Traceability linked to electronic device history records (eDHR)
Implementation tip: Start with critical-to-quality (CTQ) dimensions and expand automation in phases to balance cost and regulatory compliance.

3) Sustainability: engineering gains without regulatory compromise
Sustainability is now a design requirement rather than a marketing add-on. While recycled resins are rarely permitted for patient-contact parts, energy optimization, scrap reduction, and mono-material design strategies are gaining traction [5].
High-impact levers:
- Cycle time optimization using scientific molding and hot runner balancing
- Servo-driven electric presses with predictive heater control
- Cleanroom right-sizing to avoid over-specification
- End-of-life design: snap-fits, reduced chemistries, recyclable housings
Visit Micro Systems 2024 CSR Report
4) Regulatory and quality updates shaping 2025
The regulatory landscape is evolving, with three key drivers:
- United States – FDA QMSR: The Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR) now aligns 21 CFR Part 820 with ISO 13485, impacting supplier controls, traceability, and risk management [6].
- ISO 13485 – 2025 systematic review: Changes may be introduced based on the 2025 review; manufacturers should maintain flexible quality procedures [7].
- European Union – MDR: Increased scrutiny and documentation demands continue to affect moulders supplying the EU market [8].
Recommended actions:
- Update validation templates (IQ/OQ/PQ) to align with QMSR and ISO 13485
- Conduct gap analyzes for supplier controls and traceability
- Anticipate longer lead times for EU MDR conformity assessments
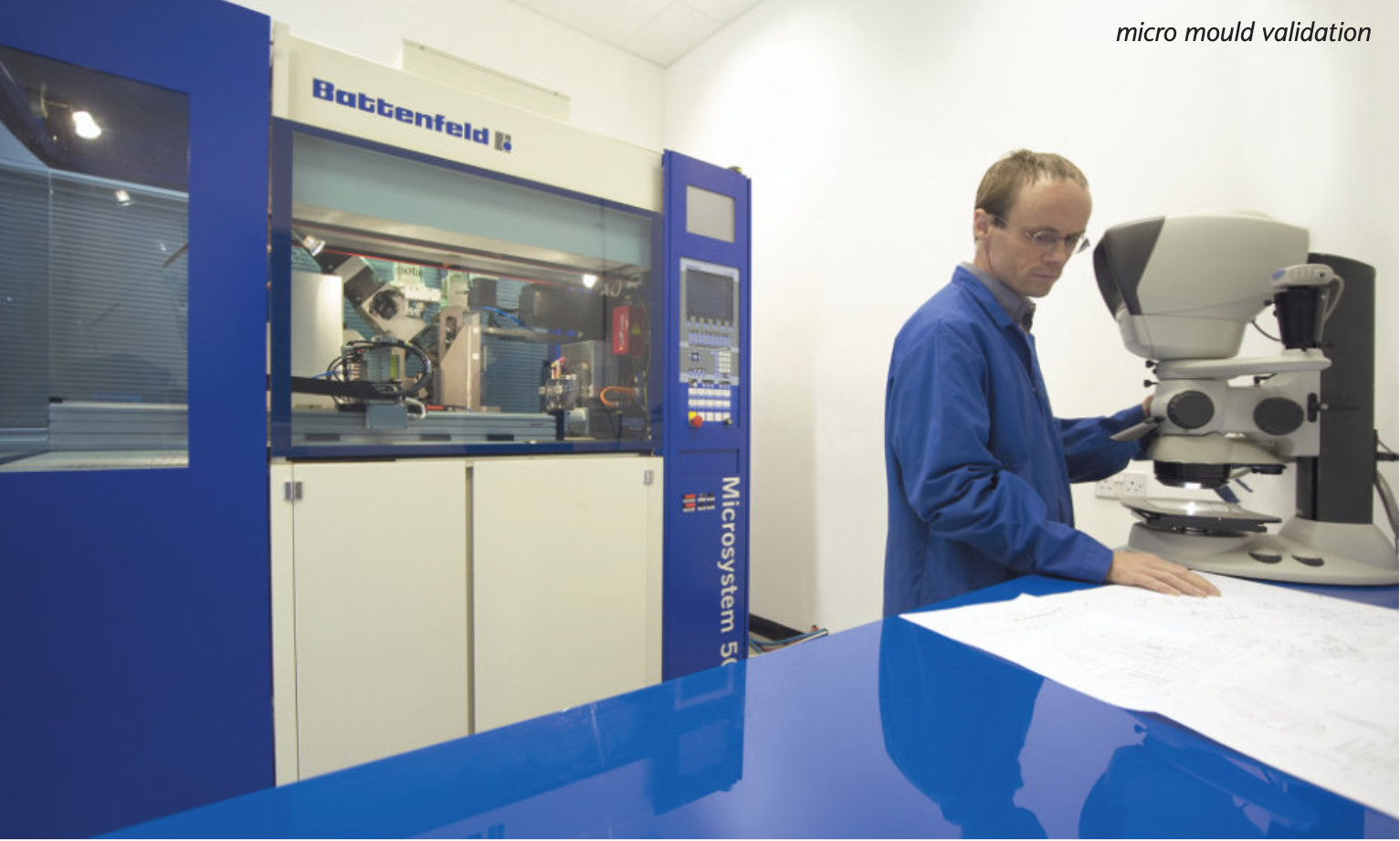

5) Materials and process innovations to watch
- COC/COP for optical and diagnostic applications
- High-modulus, high-flow polymers (LCP, PPS, PEEK) for thin-wall molding
- Medical-grade LSR micro-overmolding for seals and wearable interfaces
- Conformal cooling using additive manufacturing to reduce cycle times
- Laser and hybrid surface texturing for flow and friction optimization

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the main trends in medical injection molding for 2025?
Micro molding, automation with in-line quality control, and sustainable manufacturing practices are leading the industry.
Is micro moulding the same as conventional injection molding?
No. Micro molding deals with components typically less than 1 g, with micro-scale features requiring ultra-precise tooling and inspection.
How does sustainability apply to medical molding?
It focuses on energy efficiency, waste reduction, and material optimization, rather than recycled resins in patient-contact parts.
What regulations affect medical molding in 2025?
FDA’s QMSR, the ISO 13485 systematic review, and EU MDR compliance requirements.

Micro Systems partners with OEMs to deliver precision micro molding solutions that meet the highest standards for miniaturized medical devices, from intraocular lenses to complex drug delivery components. With in-house expertise in high-cavity micro tooling, cleanroom production, and automation integration, including in-line inspection, digital process control, and traceability, Micro Systems helps accelerate time-to-market while maintaining regulatory compliance. Its focus on sustainability includes optimizing cycle times, reducing waste through advanced hot runner design, and employing energy-efficient electric presses, enabling OEMs to achieve both quality and environmental objectives without compromising patient safety.
References
[1] Global Micro Injection Moulding Market Report 2024–2030
[2] “Micro Moulding in Medical Devices: Market Dynamics and Applications,” MedTech Insights, 2024
[3] Market Data Forecast: Medical Micro Injection Moulding Industry Outlook 2025–2033
[4] “Automation and Digitalisation in Medical Manufacturing,” Journal of Advanced Manufacturing, 2024
[5] “Sustainable Practices in Medical Injection Moulding,” Medical Plastics News, 2024
[6] U.S. Food and Drug Administration, “Quality Management System Regulation (QMSR) Final Rule,” 2024
[7] ISO/TC 210 Systematic Review Summary – ISO 13485:2016, 2025
[8] European Commission, “EU MDR Implementation Progress Report,” 2025