Overmolding medical devices: An emerging trend in MedTech 2025
Overmolding, the process of molding a secondary layer of material over a substrate, has become a transformative technique in medical device manufacturing. By combining functional, ergonomic, and aesthetic benefits, overmolding addresses growing demands for miniaturization, patient comfort, and regulatory compliance in healthcare.
Benefits of overmolding in medical devices
Ergonomics and aesthetics
Overmolding improves tactile grip, enabling clinicians to maintain control even in high-stress environments or while wearing gloves. Enhanced grip is crucial in precision-based procedures where safety and accuracy are paramount (Big News Network, 2024). The technique also allows for colour coding and soft-touch finishes, improving usability and reducing patient anxiety, particularly in devices for paediatric applications.
Durability and chemical resistance
Devices are exposed to repeated sterilization and harsh chemical environments. Overmolded layers add robustness, cushioning instruments against shocks while resisting degradation, thereby extending service life (Intech Industries, 2024; Big News Network, 2024).
Hygiene and infection control
The seamless nature of overmoulded components eliminates crevices where microorganisms could accumulate, making devices easier to sterilize and safer for clinical use (Big News Network, 2024).
Biocompatibility and patient safety
Medical-grade polymers used in overmolding are often biocompatible and latex-free, reducing risks of allergic reactions or tissue irritation in patient-contact applications (GlobeNewswire, 2024).
Cost efficiency
Although tooling costs can be high, overmolding reduces assembly requirements, consolidates parts, and improves longevity, which collectively deliver long-term economic benefits (Healthcare Guys, 2023; Big News Network, 2024).
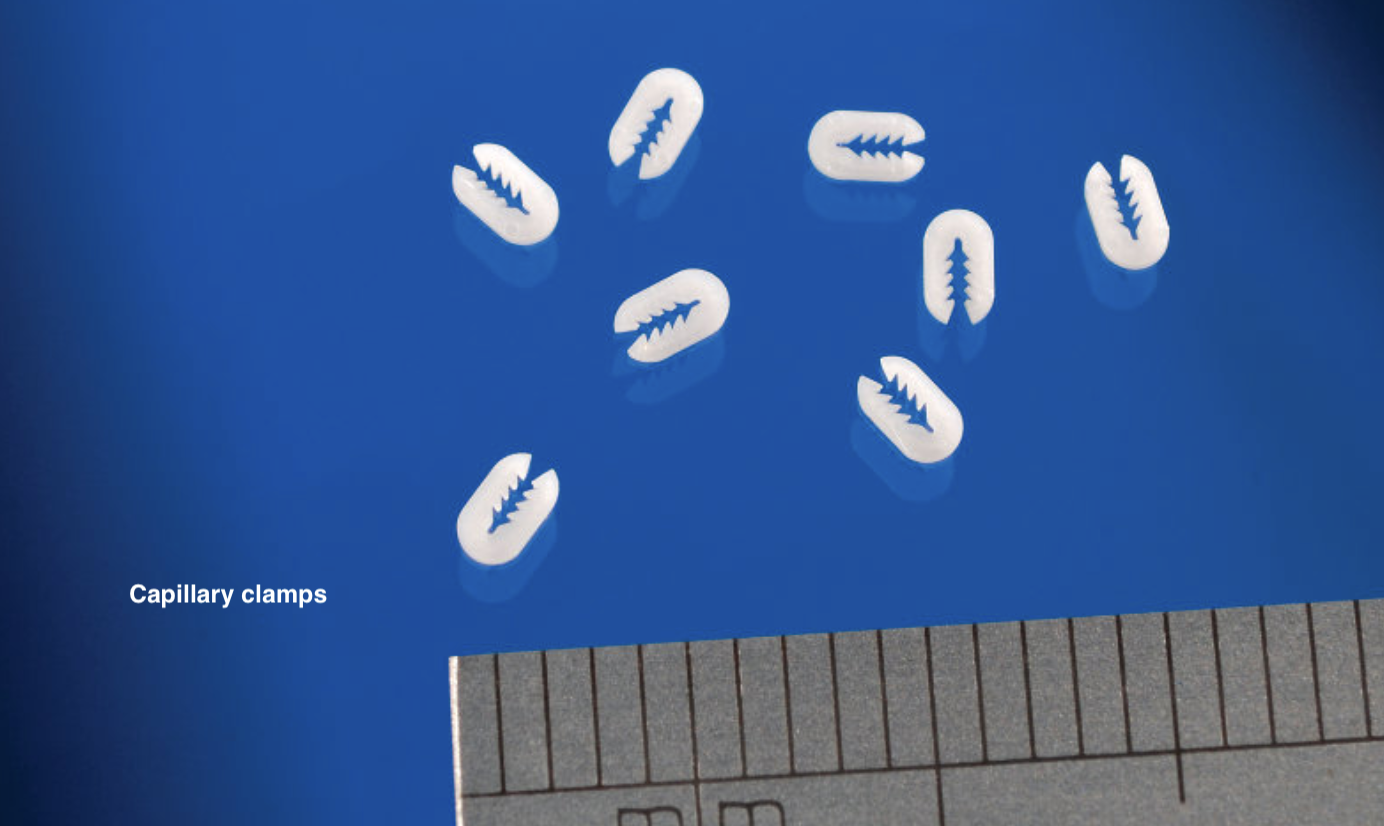

Technological trends shaping overmolding 2025
Miniaturization and micro molding
The push towards minimally invasive procedures and implantable devices has driven demand for micro-scale overmolding. This enables encapsulation of delicate electronics in neural implants and diagnostic sensors while maintaining precision (Medical Micro Molding, 2024).
Wearables and telehealth devices
Overmolding provides flexibility, water resistance, and comfort for wearable devices, ensuring reliability in home-based healthcare and continuous patient monitoring.
Advanced materials
High-performance polymers such as PEEK, liquid crystal polymers (LCPs), and thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are increasingly used in overmoulding, offering resistance to sterilization cycles and antimicrobial properties (Medical Moulds, 2024).
Embedded electronics and smart devices
Overmolding can encapsulate sensitive sensors and circuits without compromising device usability, supporting the rise of smart diagnostic and therapeutic devices.
Sustainability in manufacturing
Environmental sustainability is shaping material selection. Bio-based and recycled polymers are entering overmolding applications, while cleanroom energy efficiency and closed-loop manufacturing systems further reduce environmental impact.
Market drivers
Demand for minimally invasive and home-care solutions
With an ageing population and rising prevalence of chronic illnesses, demand for minimally invasive devices with ergonomic, comfortable designs is increasing. Overmolding meets these expectations, particularly in long-term use devices such as catheters (Research and Markets, 2024; GlobeNewswire, 2024).
Regulatory standards and patient safety
International standards and FDA guidance emphasise device usability and patient safety. Overmolding supports compliance by providing safer, more intuitive products with improved traceability (Medical Plastics News, 2024; 360iResearch, 2024).
Innovation in polymer science
Ongoing advances in biocompatible polymers and antimicrobial additives are fuelling the adoption of overmolding, allowing devices to withstand aggressive clinical environments while ensuring patient safety (GlobeNewswire, 2024).

Challenges
Despite its advantages, overmolding presents challenges. High tooling costs, material compatibility issues, and complex regulatory pathways can delay adoption. Precision at micro-scale manufacturing remains technically demanding. However, advances in automation and hybrid manufacturing (such as combining additive manufacturing with injection molding) are helping to mitigate these barriers.
Conclusion
Overmolding is no longer a peripheral manufacturing process, it has become central to the design of next-generation medical devices 2025 onwards. From improved ergonomics and patient safety to compatibility with miniaturized and wearable technologies, overmolding aligns with broader trends in MedTech innovation, sustainability, and regulation. As material science and manufacturing technologies continue to evolve, overmolding is poised to remain a cornerstone of medical device design and production.
Micro Systems is the ideal partner for overmolding medical devices, offering unmatched expertise in precision tooling, medical-grade injection molding, and cleanroom manufacturing. With a strong track record in miniaturization and biocompatible materials, the company ensures regulatory compliance while delivering ergonomic, durable, and innovative solutions. By supporting clients from design and prototyping through to full-scale production, Micro Systems provides a reliable and forward-thinking approach to complex overmolding projects.
Contact us today!