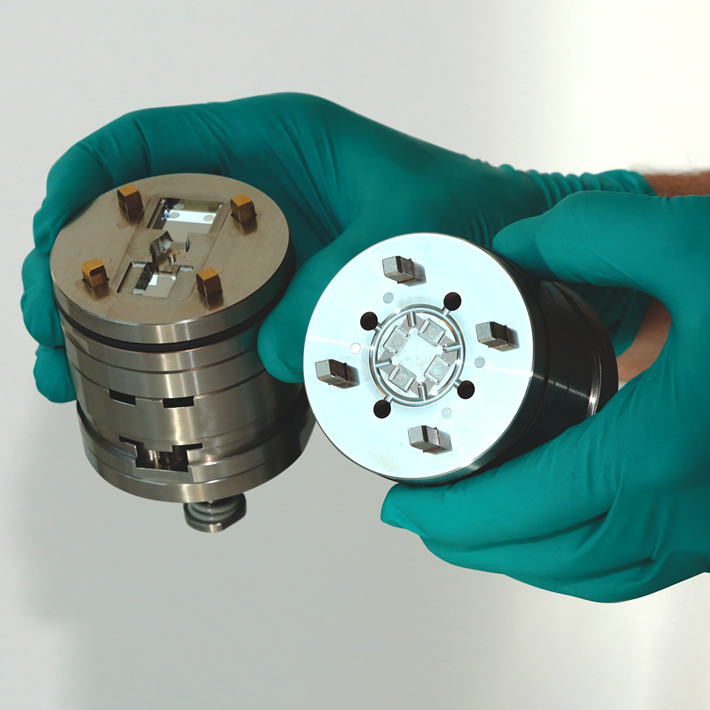
Intraocular lens manufacturing with injection molding
What is an intraocular lens (IOLs)?
An intraocular lens (IOLs) is a small, prosthetic lens for the eye. This can be done as an “upgrade” to lessen a person’s need for glasses or contact lenses, or as part of cataract surgery since the early 1980s (to replace hazy natural lenses). They are made out of two plastic side struts that support the little plastic lens within the eye. IOL implants are useful in treating vision issues including myopia (nearsightedness), hyperopia (farsightedness, presbyopia (age-related farsightedness) and astigmatism (altered eye shape).
Silicone, acrylic, or other plastic compositions are commonly used to make the majority of IOLs. Additionally, a unique substance is applied to them to assist shield eyes from the sun’s damaging ultraviolet (UV) rays. Some types of IOLs include aspheric IOLs, toric IOLs, accommodating IOLs, phakic lenses, multifocal IOLs and monovision.
According to a recent study, the intraocular lens market is predicted to increase at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.25% from 2022 to 2028, from its estimated valuation of USD 5.14 billion in 2022 to USD 7.82 billion.
How is intraocular lens (IOLs) made?
IOL manufacturing is a closely regulated process to ensure patient safety and high-quality products. IOL manufacturers are required to abide by industry standards, laws, and regulations in order to sell IOLs. A typical IOL manufacturing process includes the following steps:
- Selection of Material: A variety of materials, including silicone, acrylic, and hydrophobic acrylic, can be used to create IOLs. The surgeon’s preference, lens purpose, biocompatibility, and flexibility all play a role in the material selection process.
- IOL Design and Mold Design – Manufacture: The lens’s curvature, thickness, and other characteristics are key factors involved in the design stage, which will hence impact the mold design and mold manufacture.
- Fabrication: Precision injection molding methods are normally employed in the production of IOLs, especially for mass production projects.
- Surface Coatings: To improve optical qualities, lessen glare and increase biocompatibility, many IOLs have unique materials coated on them. Hydrophobic coatings aid in keeping water droplets from sticking to the surface of the lens.
- Quality Control: Throughout the production process, strict quality control procedures for medical products are required, including but not limited to optical testing, validation, and inspections. This step is essentially important, especially if IOLs are sold in global markets.
- Sterilisation: In order to get rid of any possible impurities, IOLs are put through sterilisation procedures after production. Ethylene oxide gas and gamma radiation are two frequently used sterilizing techniques.
- Packaging: In order to preserve their sterility until implantation, IOLs are meticulously packed in sterile, sealed containers.
Throughout the production process, mold design/manufacture and injection molding are considered to be significant, affecting the success of the mass production of the IOLs. For IOL molds, a very high degree of precision goes into the production of each and every mold, as any flaw in the mold will make its way into the final lenses as they are formed against a previously injection-molded surface. Hence, before the mass production stage, manufactured molds are tested repeatedly to ensure the injection molded lenses meet the design requirements without any error.
In contrast to mechanical components, IOLs injection molding requires specialized processing skills, and micro-molders need to have experience working with extremely small parts that have particular handling and packing needs. Within the injection molding process, or in this case micro injection molding process, a number of factors affect the reproducibility of IOLs on a mass production level. Dimensional stability is essential for distinguishing between inferior and superior IOLs, as molded lenses will not be dimensionally stable if the wrong material is used, and their effectiveness may be compromised over time due to shrinking. Close collaboration between the designers, product developers and mold maker and injection molder is hence essential when using injection molding for IOLs manufacturing as it necessitates the optimisation of design, mastering, tooling, and production processes. It is ideal to choose an injection molder with in-house tooling capabilities to increase the efficiency of the project, enhance communication and reduce production time.
Before being made available for consumer use, molded IOLs must also undergo a variety of additional manufacturing processes, including as lapping, trimming, and polishing, in order to remove any possible protrusions, pits, and edge burrs that can irritate the eyes. It is imperative that all molding and post-molding procedures guarantee that plasticisers, mold release agents, lubricants, and antioxidants do not contaminate the lens.
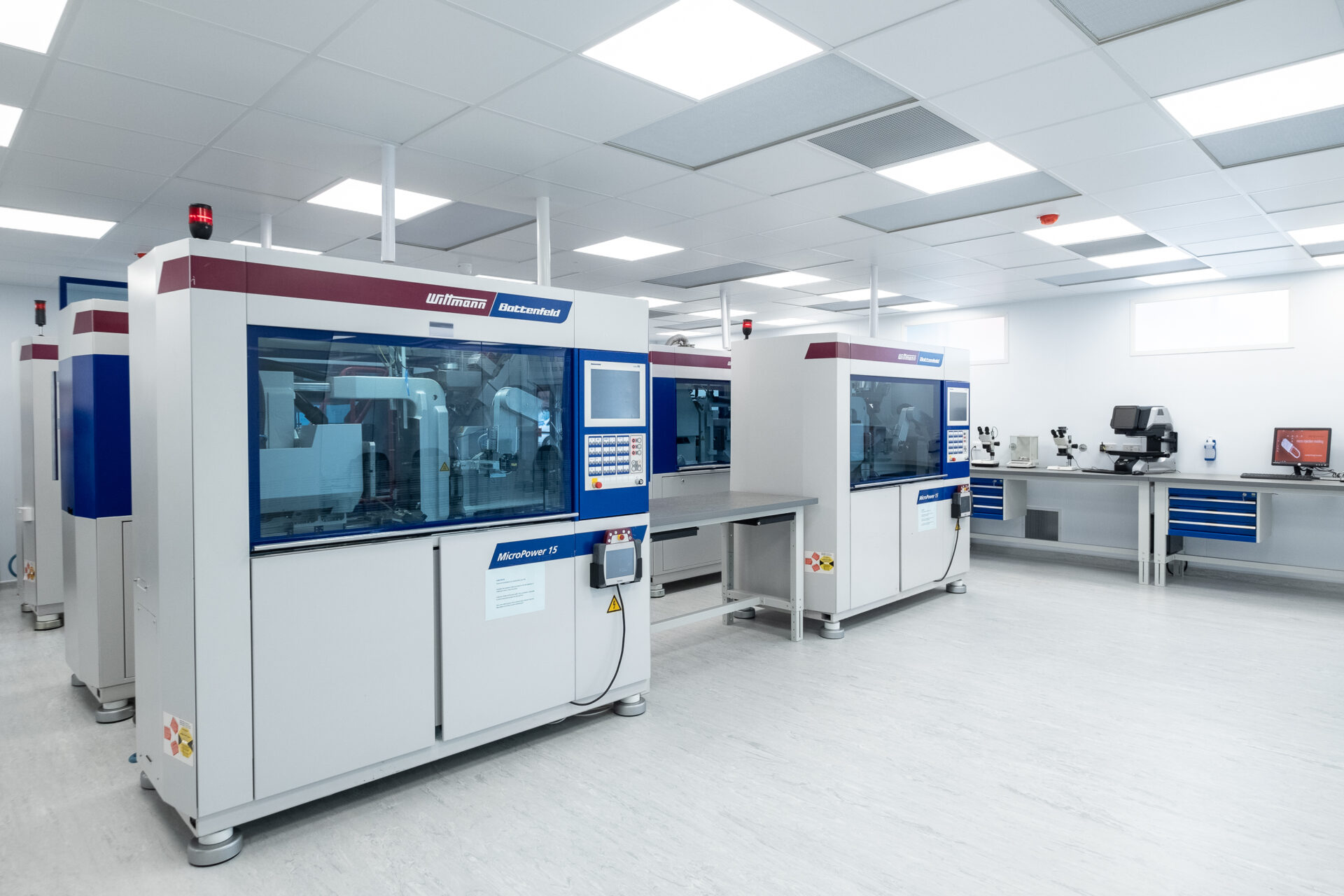
In addition, as the lens’s ability to operate may be impacted by both human and airborne pollutants, such as germs and dust from raw materials, the production of ultra-precision molds and the injection molding process are conducted within strictly controlled environments, for example ISO class 7 or 8 cleanroom environments, to ensure the highest medical quality.
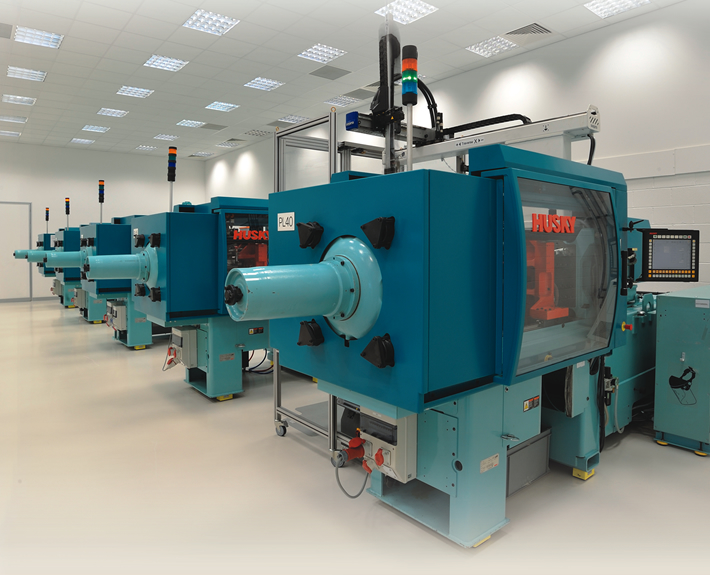

With more than 20 years of experience in micro mold toolings and injection molding, Micro Systems can support your IOL projects from the very first step, ensuring a smooth transition from prototyping to mass production. We have the latest technology in micromachining and micro injection molding, with top-of-the-field designers and engineers, and world class facilities in the UK and Singapore.
Contact us today to discuss your IOL project!